Abstract:
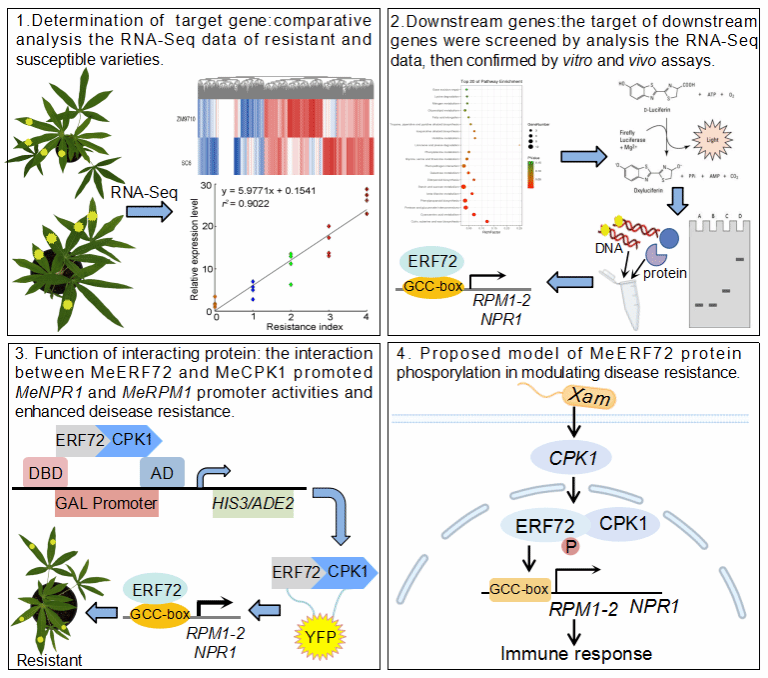
Cassava provides food and income for about billion people worldwide. However, Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis (Xam) causes cassava bacterial blight (CBB) and yield reduction worldwide in the tropics. Thus, genetic improvement between disease resistance and biomass should be finely balanced to avoid double-edged sword of some resistance genes. Ethylene response factors (ERFs) are widely involved in plant development and defense responses, whereas their possible roles in balancing plant disease resistance and biomass remain elusive, especially in cassava. Here, the transcription of MeERF72 showed higher level in disease resistant ZM9710 than that in susceptible SC6, and it positively regulated disease resistance to CBB with no effect on the biomass. Furthermore, MeERF72 directly binds to the GCC-box of target gene promoters (Nonexpressor of pathogenesis-related genes 1 (NPR1) and Resistance to pseudomonas maculicola 1-2 (RPM1-2)) to modulate their transcriptions. In addition, calcium-dependent protein kinase 1 (CPK1) interacted with and phosphorylated MeERF72 at Ser40. Interestingly, MeCPK1-MeERF72 protein interaction and phosphorylation module fine-tuned the transcription of downstream defense genes and disease resistance.
全文链接:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/pbi.14151