Abstract
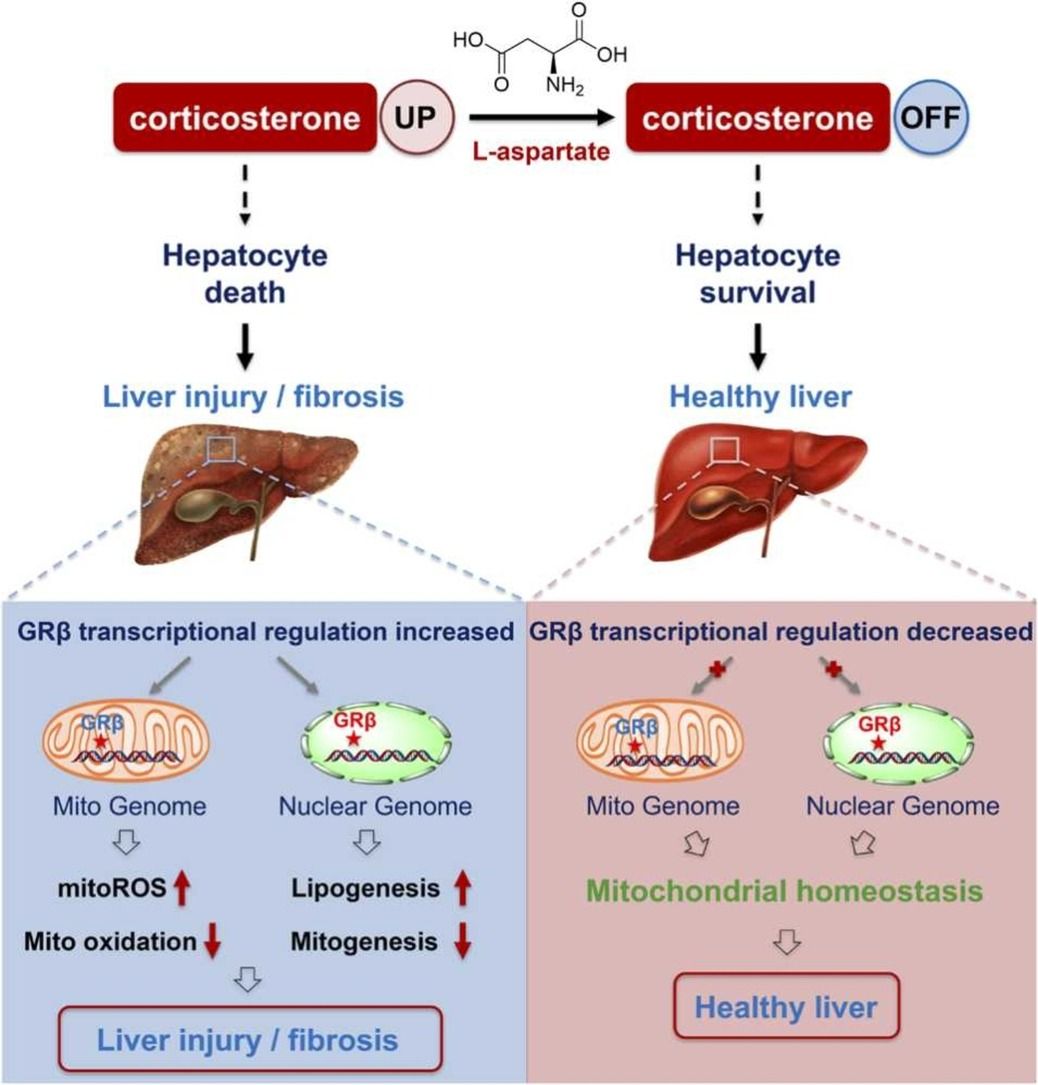
Liver fibrosis is a determinant-stage process of many chronic liver diseases and affected over 7.9 billion populations worldwide with increasing demands of ideal therapeutic agents. Discovery of active molecules with anti-hepatic fibrosis efficacies presents the most attacking filed. Here, we revealed that hepatic L-aspartate levels were decreased in CCl4-induced fibrotic mice. Instead, supplementation of L-aspartate orally alleviated typical manifestations of liver injury and fibrosis. These therapeutic efficacies were alongside improvements of mitochondrial adaptive oxidation. Notably, treatment with L-aspartate rebalanced hepatic cholesterol-steroid metabolism and reduced the levels of liver-impairing metabolites, including corticosterone (CORT). Mechanistically, L-aspartate treatment efficiently reversed CORT-mediated glucocorticoid receptor β (GRβ) signaling activation and subsequent transcriptional suppression of the mitochondrial genome by directly binding to the mitochondrial genome. Knockout of GRβ ameliorated corticosterone-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction and hepatocyte damage which also weakened the improvements of L-aspartate in suppressing GRβ signaling. These data suggest that L-aspartate ameliorates hepatic fibrosis by suppressing GRβ signaling via rebalancing cholesterol-steroid metabolism, would be an ideal candidate for clinical liver fibrosis treatment.
See more: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1043661824002391